导读
医脉双语群是一个神奇的大家庭,聚集了众多爱英语的神内医生。每日大家会在群里分享一篇英文资讯/病例+医脉双语之懂你一句+最后分享一首英文歌。大家可以开心的翻译、交流、学习,每个人都有其独特的翻译风格,每个人都在积极的参与着。今后的日子我们将不忘初心、砥砺前行。
医脉双语之懂你两句
今日鸡汤两碗:[1] Love can’t be touched, but you can feel the sweetness of her.
➤爱是无法触摸的,但你可以用心感受她的甜蜜
➤爱无影,但有形
➤虽天各一方,但柔情蜜意浓
➤真爱无形,泽被心灵。
➤两情若是长久时,又岂在朝朝暮暮
➤爱是心与心的交融
➤爱是摸不着的,但你却能感受到她带来的甜蜜
➤爱是触摸不及,而是发自内心的那份甜蜜感
➤爱情飘渺难触及,点滴甜蜜记心头
➤爱虽不能触摸但其甜蜜却能感受到
➤爱虽不能被触碰到,但你却能感受到它的轻抚
——译者:临泉县人民医院神内宋佑勇、山东省立医院放射科董印、阿杜、辽健集团铁煤总医院神内陈建国、杭师大附院王小川、顺德均安医院何深文、绿叶、廊坊市人民医院神内科袁淑珍等
[2] You mustn’t be afraid to dream a little bigger.
➤心有多大,世界就有多大
➤心有多大,梦想就有多大
➤既然做梦,那就做大点
➤不要害怕,可以梦想距离现实稍大一点
➤只有想不到,没有做不到
➤别被现实所缚,梦想可以更大一点
➤心有梦想,无所畏惧
➤敬畏梦想,相信梦想
➤解开心锁,大胆逐梦
➤追逐梦想,不负此生
➤我,是我生活的主角,心有多大,舞台就有多大
——译者:晓曼、李瑞杰、廊坊市人民医院神内科袁淑珍、辽健集团铁煤总医院神内陈建国、湘雅二詹琼、春华秋实、高明人医李欣、顺德均安医院何深文、扶沟县医院神内梁丙寅、南部战区总医院康健捷小鱼鱼、明明等
双语资讯
[1] Mortality, morbidity, and risk factors in China and its provinces, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017
➤中国及其省份的死亡率、发病率和风险因素1990-2017:2017年全球疾病负担研究的系统分析
➤ 1990-2017年中国及各省人口疾病的死亡率、发病率及风险因素:一项关于2017年全球疾病负担研究的系统分析
[2] Background
Public health is a priority for the Chinese Government. Evidence-based decision making for health at the province level in China, which is home to a fifth of the global population, is of paramount importance. This analysis uses data from the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study (GBD) 2017 to help inform decision making and monitor progress on health at the province level.
➤背景:公共卫生是中国政府的一项重点工作。中国是全球五分之一人口的聚居地,在省级卫生领域,基于证据的决策至关重要。本分析使用2017年《全球疾病、伤害和风险因素负担研究》(GBD)的数据,帮助制定决策并监测省级卫生事业进展。
[3] Methods
We used the methods in GBD 2017 to analyse health patterns in the 34 province-level administrative units in China from 1990 to 2017. We estimated all-cause and cause-specific mortality, years of life lost (YLLs), years lived with disability (YLDs), disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs), summary exposure values (SEVs), and attributable risk. We compared the observed results with expected values estimated based on the Socio-demographic Index (SDI).
➤方法:该研究采用GBD2017方法,对1990-2017年全国34个省级行政单位的卫生状况进行了分析。研究估计了全因和特定原因死亡率、寿命损失年数(YLLs)、残疾生活年数(YLDs)、残疾调整寿命年数(DALYs)、总暴露值(SEVs)和可归因风险,并将观察到的结果与基于社会人口指数(SDI)估计的期望值进行了比较。
[4] Findings
Stroke and ischaemic heart disease were the leading causes of death and DALYs at the national level in China in 2017. Age-standardised DALYs per 100 000 population decreased by 33•1% (95% uncertainty interval [UI] 29•8 to 37•4) for stroke and increased by 4•6% (–3•3 to 10•7) for ischaemic heart disease from 1990 to 2017. Age-standardised stroke, ischaemic heart disease, lung cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and liver cancer were the five leading causes of YLLs in 2017.
➤结果:卒中和缺血性心脏病是2017年全国范围内死亡和DALYs的主要原因。从1990年到2017年,每10万人的年龄标准化DALYs降低了33.1%(95%不确定度[UI] 29.8- 37.4),缺血性心脏病增加了4.6%(-3.3-10.7)。年龄标准化卒中,缺血性心脏病,肺癌,慢性阻塞性肺病和肝癌是2017年YLLs的五大主要原因。
[5] Musculoskeletal disorders, mental health disorders, and sense organ diseases were the three leading causes of YLDs in 2017, and high systolic blood pressure, smoking, high-sodium diet, and ambient particulate matter pollution were among the leading four risk factors contributing to deaths and DALYs. All provinces had higher than expected DALYs per 100 000 population for liver cancer, with the observed to expected ratio ranging from 2•04 to 6•88.
➤肌肉骨骼疾病、精神健康疾病和感觉器官疾病是2017年YLDS的三大主要原因,收缩压高、吸烟、高钠饮食和环境颗粒物污染是导致死亡和DALYS的四大危险因素。各省每10万人的肝癌DALYs均高于预期,观察到的与预期的比率为2.04-6.88。
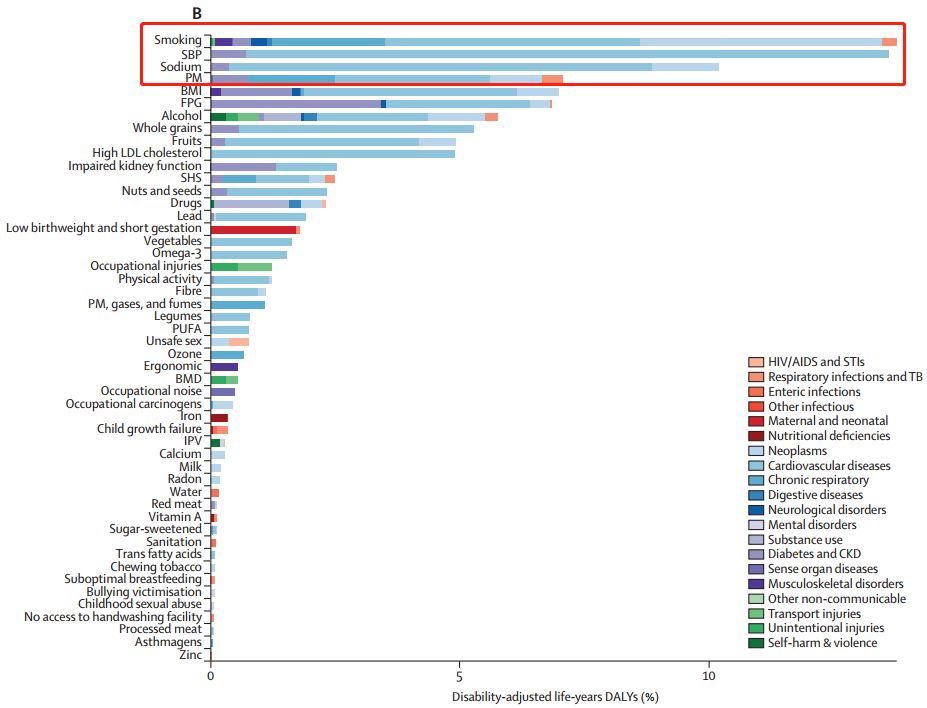
[6] The all-cause age-standardised DALYs per 100 000 population were lower than expected in all provinces in 2017, and among the top 20 level 3 causes were lower than expected for ischaemic heart disease, Alzheimer’s disease, headache disorder, and low back pain. The largest percentage change at the national level in age-standardised SEVs among the top ten leading risk factors was in high body-mass index (185%, 95% UI 113•1 to 247•7]), followed by ambient particulate matter pollution (88•5%, 66•4 to 116•4).
➤ 2017年全国10万人全因年龄标准化DALYs均低于预期,其中缺血性心脏病、阿尔茨海默病、头痛障碍和下腰痛位列前20位,均低于预期。前10大危险因素中,年龄标准化SEVs在全国水平的变化百分比最大的是高体重指数(185%,95%不确定度[UI]113.1-247.7),其次是环境颗粒物污染(88.5%,66.4 – 116.4)。
[7] Interpretation
China has made substantial progress in reducing the burden of many diseases and disabilities. Strategies targeting chronic diseases, particularly in the elderly, should be prioritised in the expanding Chinese health-care system.
➤启示:中国在减轻许多疾病和残疾负担方面取得了实质性进展。在不断扩大的中国卫生保健体系中,应对慢性病,特别是老年人的慢性病,采取优先战略。
信源:Mortality, morbidity, and risk factors in China and its provinces, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017.The Lancet Journal. Published:June 24, 2019.
——译者:大坪医院黎炳护、锦医大附属第一医院金婷等
每日音乐
今天给大家带来的是 #1 Dads的单曲《Camberwell》。#1 Dads是澳大利亚音乐人,是一个前卫的艺术家。
部分歌词☟☟☟
The morning leads me over to my window.
清晨将我牵到窗前
The air feels sharp against my skin.
空气伸出锐利的手碰我
Am I leaning out, or the outside leaning in
是我正向外探去,还是外面正探进我来?
the streets in the city where I sleep.
街道在我安然入睡的城市栖着
错过了群里的现场讨论,千万不要错过小编的笔记哦~想进入医脉双语群的医友们可加小脉微信(medlive_xiaomai),申请加入双语群即可~如果您有更准确的或优美的句子来描述这些内容也可以留言哦~
往期精彩
限 时 特 惠: 本站每日持续更新海量各大内部创业教程,一年会员只需98元,全站资源免费下载 点击查看详情
站 长 微 信: lzxmw777