回复【哪吒】,加入Java技术交流群
一、@Async注解
@Async的作用就是异步处理任务。
在方法上添加@Async,表示此方法是异步方法;
在类上添加@Async,表示类中的所有方法都是异步方法;
使用此注解的类,必须是Spring管理的类;
需要在启动类或配置类中加入@EnableAsync注解,@Async才会生效;
在使用@Async时,如果不指定线程池的名称,@Async有默认线程池,使用的是Spring默认的线程池SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor。
默认线程池的默认配置如下:
默认核心线程数:8;
最大线程数:Integet.MAX_VALUE;
队列使用LinkedBlockingQueue;
容量是:Integet.MAX_VALUE;
空闲线程保留时间:60s;
线程池拒绝策略:AbortPolicy;
从最大线程数可以看出,在并发情况下,会无限制的创建线程。
也可以通过yml重新配置:
spring:
task:
execution:
pool:
max-size: 10
core-size: 5
keep-alive: 2s
queue-capacity: 1000
thread-name-prefix: my-executor
也可以自定义线程池,下面通过简单的代码来实现@Async自定义线程池。
二、代码实例1、导入POM
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.guava</groupId>
<artifactId>guava</artifactId>
<version>30.1.1-jre</version>
</dependency>
2、配置类AsyncTaskConfig
package com.nezhac.config;
import com.google.common.util.concurrent.ThreadFactoryBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
@EnableAsync
@Configuration
public class AsyncTaskConfig {
/**
* 方式1
* com.google.guava中的线程池
* @return
*/
@Bean("my-executor")
public Executor firstExecutor() {
ThreadFactory threadFactory = new ThreadFactoryBuilder().setNameFormat("my-executor").build();
// 获取CPU的处理器数量
int curSystemThreads = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() * 2;
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(curSystemThreads, 100,
200, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue(), threadFactory);
threadPool.allowsCoreThreadTimeOut();
return threadPool;
}
/**
* 方式2
* Spring线程池
* @return
*/
@Bean("async-executor")
public Executor asyncExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor taskExecutor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
// 核心线程数
taskExecutor.setCorePoolSize(10);
// 线程池维护线程的最大数量,只有在缓冲队列满了之后才会申请超过核心线程数的线程
taskExecutor.setMaxPoolSize(100);
// 缓存队列
taskExecutor.setQueueCapacity(50);
// 空闲时间,当超过了核心线程数之外的线程在空闲时间到达之后会被销毁
taskExecutor.setKeepAliveSeconds(200);
// 异步方法内部线程名称
taskExecutor.setThreadNamePrefix("async-executor-");
/**
* 当线程池的任务缓存队列已满并且线程池中的线程数目达到maximumPoolSize,如果还有任务到来就会采取任务拒绝策略
* 通常有以下四种策略:
* ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy:丢弃任务,抛出RejectedExecutionException异常。
* ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy:丢弃任务,但不抛出异常。
* ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy:丢弃队列最前面的任务,然后重新尝试重新执行任务。
* ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy:重试添加当前的任务,自动重复调用 execute() 方法,直到成功。
*/
taskExecutor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
taskExecutor.initialize();
return taskExecutor;
}
}
3、UserController
package com.nezha.controller;
import com.nezha.service.UserService;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class UserController {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(UserController.class);
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@GetMapping("asyncTest")
public void asyncTest() {
logger.info("哪吒真帅");
userService.asyncTest();
asyncTest2();
logger.info("哪吒编程,每日更新Java干货");
}
@Async("my-executor")
public void asyncTest2() {
logger.info("同文件内执行执行异步任务");
}
}
4、UserService
package com.nezha.service;
public interface UserService {
// 普通方法
void test();
// 异步方法
void asyncTest();
}
UserServiceImpl
package com.nezha.service;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(UserServiceImpl.class);
@Override
public void test() {
logger.info("执行普通任务");
}
@Async("my-executor")
@Override
public void asyncTest() {
logger.info("执行异步任务");
}
}

三、发现同文件内执行异步任务,还是一个线程,没有实现@Async效果,why?
众里寻他千百度,查到了@Async失效的几个原因:
调用方和@Async方法在一个类中;
没加@EnableAsync注解;
注解@Async的返回值只能为void或Future;
注解@Async的方法不能是public方法;
注解@Async方法使用static修饰也会失效;
在Async方法上标注@Transactional是没用的,但在Async方法调用的方法上标注@Transcational是有效的;
四、配置中分别使用了ThreadPoolTaskExecutor和ThreadPoolExecutor,这两个有啥区别?
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor是spring core包中的,而ThreadPoolExecutor是JDK中的JUC。
1、initialize()
查看一下ThreadPoolTaskExecutor 的 initialize()方法
public abstract class ExecutorConfigurationSupport extends CustomizableThreadFactory
implements BeanNameAware, InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
...
/**
* Set up the ExecutorService.
*/
public void initialize() {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Initializing ExecutorService" + (this.beanName != null ? " '" + this.beanName + "'" : ""));
}
if (!this.threadNamePrefixSet && this.beanName != null) {
setThreadNamePrefix(this.beanName + "-");
}
this.executor = initializeExecutor(this.threadFactory, this.rejectedExecutionHandler);
}
/**
* Create the target {@link java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService} instance.
* Called by {@code afterPropertiesSet}.
* @param threadFactory the ThreadFactory to use
* @param rejectedExecutionHandler the RejectedExecutionHandler to use
* @return a new ExecutorService instance
* @see #afterPropertiesSet()
*/
protected abstract ExecutorService initializeExecutor(
ThreadFactory threadFactory, RejectedExecutionHandler rejectedExecutionHandler);
...
}
2、initializeExecutor抽象方法
再查看一下initializeExecutor抽象方法的具体实现类,其中有一个就是ThreadPoolTaskExecutor类,查看它的initializeExecutor方法,使用的就是ThreadPoolExecutor。
public class ThreadPoolTaskExecutor extends ExecutorConfigurationSupport
implements AsyncListenableTaskExecutor, SchedulingTaskExecutor {
...
@Override
protected ExecutorService initializeExecutor(
ThreadFactory threadFactory, RejectedExecutionHandler rejectedExecutionHandler) {
BlockingQueue queue = createQueue(this.queueCapacity);
ThreadPoolExecutor executor;
if (this.taskDecorator != null) {
executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
this.corePoolSize, this.maxPoolSize, this.keepAliveSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
queue, threadFactory, rejectedExecutionHandler) {
@Override
public void execute(Runnable command) {
Runnable decorated = taskDecorator.decorate(command);
if (decorated != command) {
decoratedTaskMap.put(decorated, command);
}
super.execute(decorated);
}
};
}
else {
executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
this.corePoolSize, this.maxPoolSize, this.keepAliveSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
queue, threadFactory, rejectedExecutionHandler);
}
if (this.allowCoreThreadTimeOut) {
executor.allowCoreThreadTimeOut(true);
}
this.threadPoolExecutor = executor;
return executor;
}
...
}
因此可以了解到ThreadPoolTaskExecutor是对ThreadPoolExecutor进行了封装。
五、核心线程数
配置文件中的线程池核心线程数为何配置为
// 获取CPU的处理器数量
int curSystemThreads = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() * 2;
Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()获取的是CPU核心线程数,也就是计算资源。
在实际中,需要对具体的线程池大小进行调整,可以通过压测及机器设备现状,进行调整大小。如果线程池太大,则会造成CPU不断的切换,对整个系统性能也不会有太大的提升,反而会导致系统缓慢。
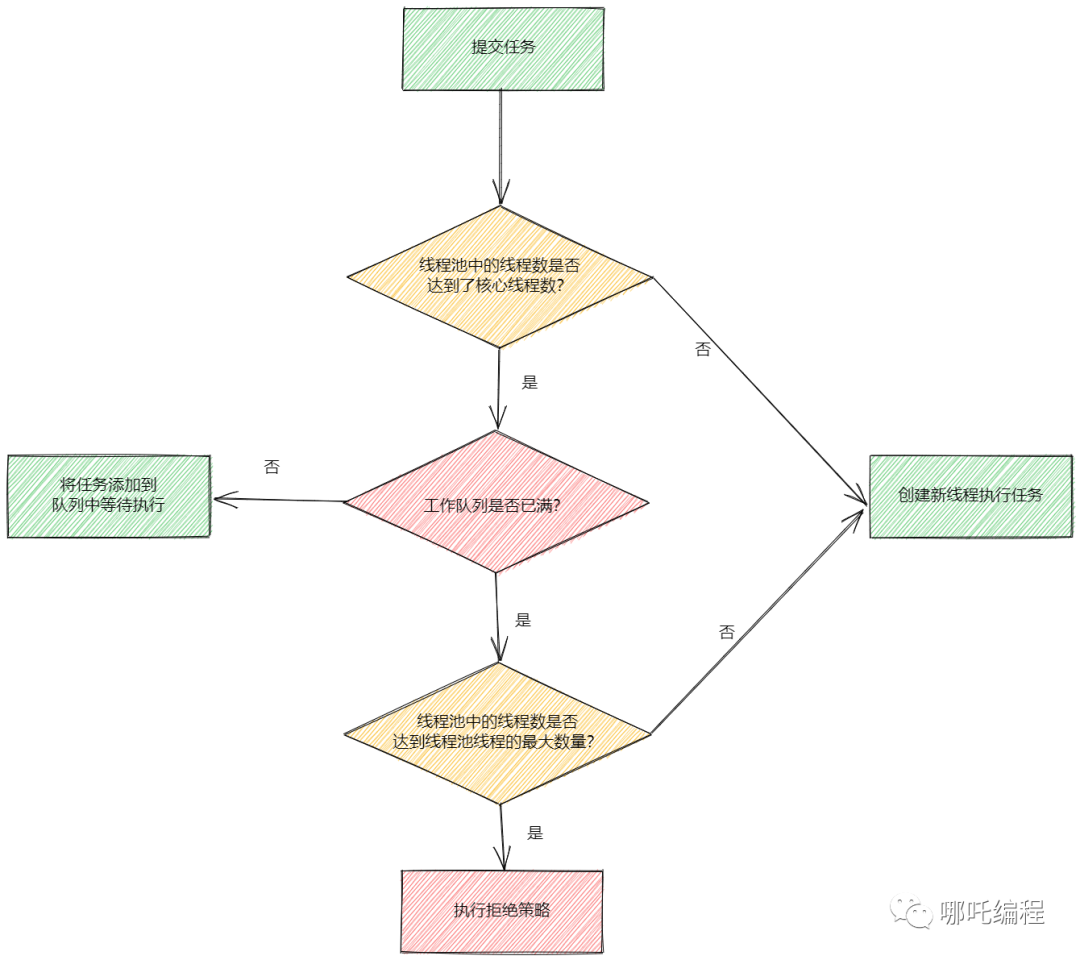
六、线程池执行流程
七、跟闪电侠学 Netty
这是一本专门为 Netty 初学者打造的入门及进阶学习图书,无论你之前有没有使用过 Netty,都可以从本书中有所收获。本书分上下两篇。上篇通过一个即时聊天系统的实战案例,让读者能够系统地使用一遍 Netty,全面掌握 Netty 的知识点;下篇通过对源码的层层剖析,让读者能够掌握 Netty 底层原理,知其然并知其所以然,从而编写出高性能网络应用程序。如果你想全面系统地学习 Netty,并掌握一些性能调优方法,本书上篇可以帮助你完成这个目标。如果你想深入了解 Netty 的底层设计,编写出更灵活高效的网络通信程序,本书下篇可以帮助你完成这个目标。如果你从未读过开源框架源码,本书将是你的第一本源码指导书,读源码并不难,难的是迈出这一小步,之后就能通往更广阔的世界。
限 时 特 惠: 本站每日持续更新海量各大内部创业教程,一年会员只需98元,全站资源免费下载 点击查看详情
站 长 微 信: lzxmw777