github.com/mqyqingfeng/Blog/issues/14
类数组对象
所谓的类数组对象:
拥有一个 length 属性和若干索引属性的对象
举个例子:
vararray = [‘name’,’age’,’sex’];
vararrayLike = {
0: ‘name’,
1: ‘age’,
2: ‘sex’,
length: 3
即便如此,为什么叫做类数组对象呢?
那让我们从读写、获取长度、遍历三个方面看看这两个对象。
读写
console.log(array[0]);// name
console.log(arrayLike[0]);// name
array[0] = ‘new name’;
arrayLike[0] = ‘new name’;
长度
console.log(array.length);// 3
console.log(arrayLike.length);// 3
遍历
for(vari = 0,len = array.length;ilen;i++){
……
for(vari = 0,len = arrayLike.length;ilen;i++){
……
是不是很像?
那类数组对象可以使用数组的方法吗?比如:
arrayLike.push(‘4’);
然而上述代码会报错: arrayLike.push is not a function
所以终归还是类数组呐……
调用数组方法
如果类数组就是任性的想用数组的方法怎么办呢?
既然无法直接调用,我们可以用 Function.call 间接调用:
vararrayLike = {0: ‘name’,1: ‘age’,2: ‘sex’,length: 3}
Array.prototype.join.call(arrayLike,’&’);// name&age&sex
Array.prototype.slice.call(arrayLike,0);// [“name”, “age”, “sex”]
// slice可以做到类数组转数组
Array.prototype.map.call(arrayLike,function(item){
returnitem.toUpperCase();
});
// [“NAME”, “AGE”, “SEX”]
类数组转对象
在上面的例子中已经提到了一种类数组转数组的方法,再补充三个:
vararrayLike = {0: ‘name’,1: ‘age’,2: ‘sex’,length: 3}
// 1. slice
Array.prototype.slice.call(arrayLike);// [“name”, “age”, “sex”]
// 2. splice
Array.prototype.splice.call(arrayLike,0);// [“name”, “age”, “sex”]
// 3. ES6 Array.from
Array.from(arrayLike);// [“name”, “age”, “sex”]
// 4. apply
Array.prototype.concat.apply([],arrayLike)
那么为什么会讲到类数组对象呢?以及类数组有什么应用吗?
要说到类数组对象,Arguments 对象就是一个类数组对象。在客户端 JavaScript 中,一些 DOM 方法(document.getElementsByTagName()等)也返回类数组对象。
Arguments对象
接下来重点讲讲 Arguments 对象。
Arguments 对象只定义在函数体中,包括了函数的参数和其他属性。在函数体中,arguments 指代该函数的 Arguments 对象。
举个例子:
functionfoo(name,age,sex){
console.log(arguments);
foo(‘name’,’age’,’sex’)
打印结果如下:
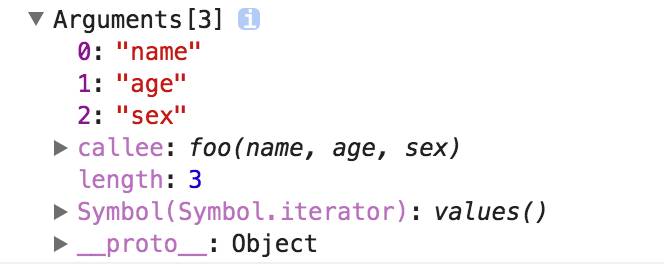
我们可以看到除了类数组的索引属性和length属性之外,还有一个callee属性,接下来我们一个一个介绍。
length属性
Arguments对象的length属性,表示实参的长度,举个例子:
functionfoo(b,c,d){
console.log(“实参的长度为:” + arguments.length)
console.log(“形参的长度为:” + foo.length)
foo(1)
// 形参的长度为:3
// 实参的长度为:1
callee属性
Arguments 对象的 callee 属性,通过它可以调用函数自身。
讲个闭包经典面试题使用 callee 的解决方法:
vardata = [];
for(vari = 0;i3;i++){
(data[i] = function(){
console.log(arguments.callee.i)
}).i = i;
data[0]();
data[1]();
data[2]();
// 0
// 1
// 2
接下来讲讲 arguments 对象的几个注意要点:
arguments 和对应参数的绑定
functionfoo(name,age,sex,hobbit){
console.log(name,arguments[0]);// name name
// 改变形参
name = ‘new name’;
console.log(name,arguments[0]);// new name new name
// 改变arguments
arguments[1] = ‘new age’;
console.log(age,arguments[1]);// new age new age
// 测试未传入的是否会绑定
console.log(sex);// undefined
sex = ‘new sex’;
console.log(sex,arguments[2]);// new sex undefined
arguments[3] = ‘new hobbit’;
console.log(hobbit,arguments[3]);// undefined new hobbit
foo(‘name’,’age’)
传入的参数,实参和 arguments 的值会共享,当没有传入时,实参与 arguments 值不会共享
除此之外,以上是在非严格模式下,如果是在严格模式下,实参和 arguments 是不会共享的。
传递参数
将参数从一个函数传递到另一个函数
// 使用 apply 将 foo 的参数传递给 bar
functionfoo(){
bar.apply(this,arguments);
functionbar(a,b,c){
console.log(a,b,c);
foo(1,2,3)
强大的ES6
使用ES6的 … 运算符,我们可以轻松转成数组。
functionfunc(…arguments){
console.log(arguments);// [1, 2, 3]
func(1,2,3);
应用
arguments的应用其实很多,在下个系列,也就是 JavaScript 专题系列中,我们会在 jQuery 的 extend 实现、函数柯里化、递归等场景看见 arguments 的身影。这篇文章就不具体展开了。
如果要总结这些场景的话,暂时能想到的包括:
参数不定长
函数柯里化
递归调用
函数重载
…
限 时 特 惠: 本站每日持续更新海量各大内部创业教程,一年会员只需98元,全站资源免费下载 点击查看详情
站 长 微 信: lzxmw777